Applications of Organic Chemistry
The reason you are enrolled in CHEM 312 is not to become Organic Chemists, but to recognize and apply organic chemistry within your discipline! There will be a heavy focus throughout the quarter on finding these applications of Organic Chemistry. These topics will change quarter to quarter to match the expertise of your instructor, but also to match the interests of the class! Below are some learning goals/outcomes for each application topic that you may see.
Bio-Organic Chemistry
- Lipids
- Identify the hydrophilic and hydrophobic sections of a lipid
- Understand the concept of surfactants (hydrophilic/hydrophobic, micelles, cell walls)
- Identify saturated, unsaturated, and trans fats
- Proteins
- Be able to identify the basic structure of an amino acid
- Not memorize individual amino acids, but know the general framework
- Given a polypeptide, be able to identify the peptide bond
- Know the difference between an alpha helix and a beta sheet
- Be able to identify the basic structure of an amino acid
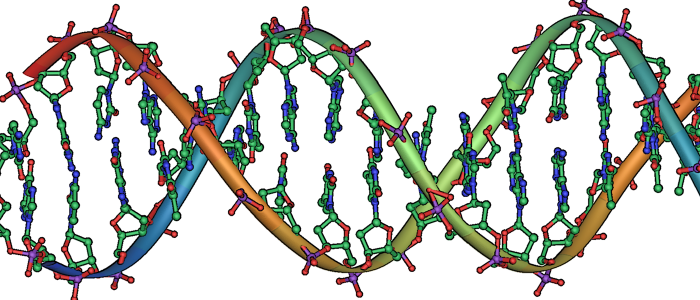
- DNA & RNA
- Describe how base pairs bond to each other and the role of Hydrogen Bonding
- Identify the bases by structure in DNA & RNA
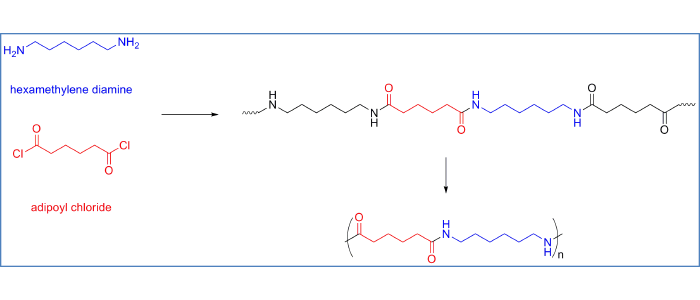
Organic Polymers
- Represent polymers as repeating units
- Identify the monomers used to construct different polymers
- Identify common materials & applications of Polymer Science
- Describe the meaning of different recycling codes
- Biodegradable polymers as an alternative to many non-degradable polymers
- Identify the difference between addition (chain-growth) and condensation (step-growth) polymerizations
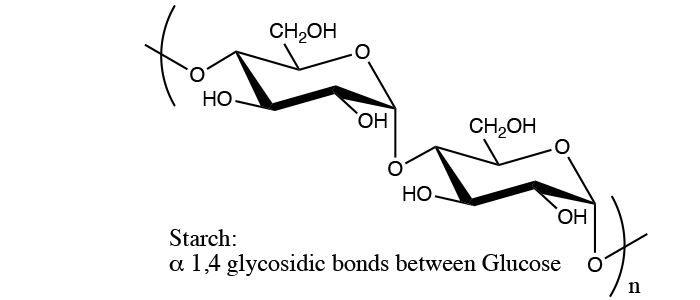
Carbohydrates
- Connect D or L to stereochemistry of Organic Molecules
- Identify a or b from Haworth projection or Chair Structures
- Show and explain how a and b can interconvert through acetal mechanism
- Identify the anomeric position in a cyclic carbohydrate
- Understand the numbering system in cyclic and open-chain carbohydrates
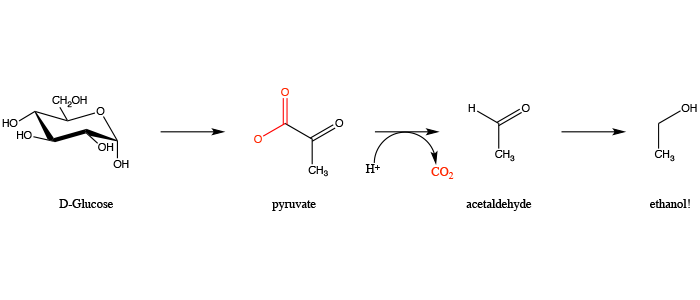
Fermentation
- Describe how a polysaccharide is converted to carbon dioxide and ethanol
- Polysaccharide to monosaccharides to pyruvate to CO2/EtOH
- Conversational in discussion
- Understand how treatments affect flavor, role of functional groups and impact on flavor
Pharmaceuticals
- Identify common drugs/relevant information
- Caffeine, Nicotine, Morphine, LSD, Viagra
- Pharmaceutical values of the naturally existing bioactive molecules
- Structure of bioactive molecules and common functional groups to those molecules
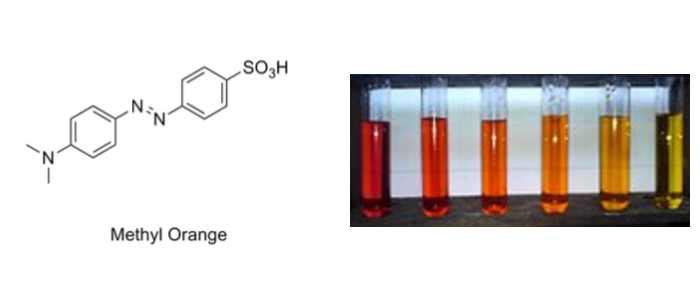
Color and Fluorescence
- Discriminate between conjugated and non-conjugated systems
- Identify sp3 hybridized carbon as a roadblock to conjugation
- Connect conjugation to the absorbance of visible light